
POSEIDON (Roman name Neptune) was the God of the sea, earthquakes and
A grandson of Zeus and son of Tantalus and Dione, the daughter of Atlas. 1 As he was thus a great-grandson of Cronus, he is called by Pindar Kronios ( Κρόνιος ), 2 though it may also contain an allusion to Pluto, the mother of Tantalus, who was a daughter of Cronus. Some writers call the mother of Pelops Euryanassa or Clytia. 3

VP (VP98508133) Twitter
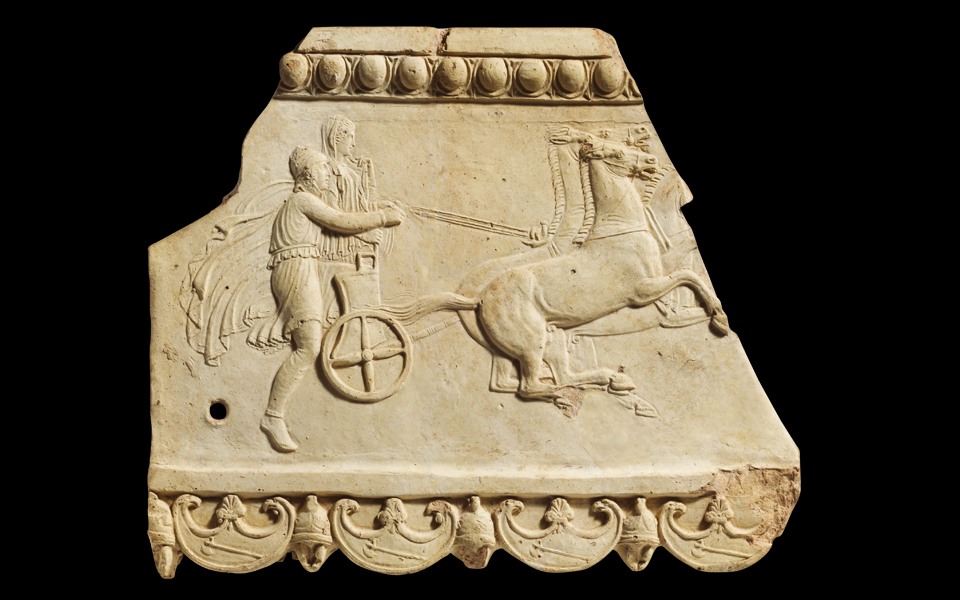
Poseidon then made Pelops his apprentice in Olympus and taught him how to steer the divine chariot. He left his homeland, Phrygia or Lydia, and went to Greece, where he participated in a chariot race against King Oenomaus of Pisa.

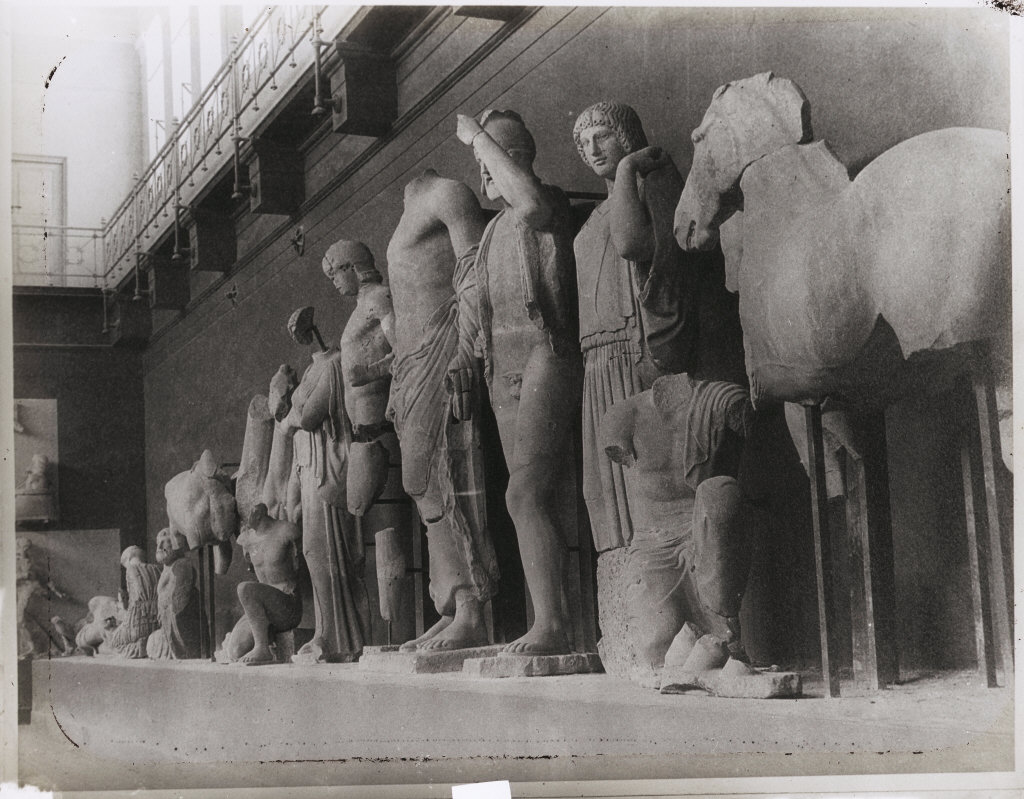
Pelops and Oenomaus swearing their vows to Zeus, eastern pediment
Updated: 01/24/2023 Pelops in Greek Mythology: Overview Pelops is a Greek mythological figure who plays a large role both on Olympus and in the human world as a King of the Peloponnesus area of.

Poseidon and Pelops Gods & Lovers Collection Etsy
P Paca'rius , De'cimus - M. Pacu'vius and Q. Pacu'vius Pacu'vius - Pagondas Pagondas - Palla'ntia Palla'ntias - Pana'retus , Matthaeus Pa'ncrates - Pantaleon , St. Pantauchus - Parcae Pardus , Gregorius - Parysatis or Parysatis Ochus Parysatis - Patri'cius Patri'cius - Paulus Paulus - Pausa'nias

Poseidon and Pelops Gods & Lovers Collection Etsy
To improve his chances, Pelops prayed first to his lover Poseidon, asking for either the world's fastest chariot, or some defense against Oenomaus' terrible spear.

Ancient Greek Gods and Heroes of the Peloponnese Greece Is
Learning of his father's atrocity, they resurrected Pelops, and Poseidon took him to Olympus as his lover and apprentice in chariot racing. Drawing upon this apprenticeship and divine favour, the hero later beat king Oenomaus of Pisa, a polis very close to Olympia, in a chariot race so as to win his daughter's hand in marriage.

Poseidon and Pelops Gods & Lovers Collection Etsy
Pelops, king of Pelepponesia and a founder of the Olympic Games Larissa, a nymph, whose three sons with Poseidon eventually ruled all of Thessaly Canace, a human woman who bore the god five children Alcyone, one of the Pleiades, who bore Poseidon several children Sexual Violence

Poseidon and Pelops (audio from the mythology guy) YouTube
Translation Dark-Eyed ( pelios, ops) PELOPS was a king of the Eleian city of Pisa and the eponymous overlord of the western Peloponnesos, the so-called "Island of Pelops". His father King Tantalos of Lydia was impious man who, wishing to test the fallibility of the gods, butchered the young Pelops and served him at a feast of the gods.

Ancient Greece Reloaded
Poseidon fulfills Pelops' prayer, and Pelops' accomplishment occurs so quickly that Pindar does not even provide a shot of Pelops competing against Oinomaos. All we see are a single image of a golden chariot and winged horses that never tire (86-87). With these gifts, it is a done deal: Pelops has won..

Myths and Mythology The Commons Pelops and Chiralan Sons offered
Pelops, legendary founder of the Pelopid dynasty at Mycenae in the Greek Peloponnese, which was probably named for him.Pelops was a grandson of Zeus, the king of the gods. According to many accounts, his father, Tantalus, cooked and served Pelops to the gods at a banquet.Only Demeter, bereaved over the loss of her daughter, failed to recognize him and partook.

Myths and Mythology The Commons Pelops and Chiralan Sons offered
The rare subjects depicted on the floor all relate to either Poseidon, Pelops, Bellerophon or Atlas, and suggest high standards of mythological knowledge and longevity of classical culture amongst the villa-owning inhabitants of late fourth-century Berkshire. The mosaic shows a connection to earlier depictions of the Pelops story, but is highly.

Pelops' chariot race Greek mythology Quatr.us Study Guides
§20. The story of the dismemberment of Pelops by Tantalos and the eating of his flesh by the gods is being ostentatiously rejected as a "false" substitute for the "true" story of the abduction and rape of Pelops by Poseidon (Pindar Olympian 1.28-29, 30-42, 46-53).

The House of Atreus, Part 1 Oral Traditions
BnF Museum (Cabinet des médailles), Paris. Poseidon ( / pəˈsaɪdən, pɒ -, poʊ -/; [1] Greek: Ποσειδῶν) is one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses. [2] He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cities and colonies.
Pelops in Greek Mythology Greek Legends and Myths
page 200 note 3 Poseidon cannot have been part of the Pelops story before Pindar, as his love replaces the former cooking (lines 25 ff.; 36 ff.; 52) and his help for Pelops (71 ff.) presupposes his love: see below. For the meaning of line 26 see Kakridis, J., Philo logus, xxxix (1930), 475.

Greek in chariot hires stock photography and images Alamy
Pelops and the Chariot Race Long ago, there was a hero named Pelops who lived in Greece. Pelops was the grandson of Zeus, and he was famous throughout the land as a brilliant chariot racer. In fact, he was so good in these races that even Poseidon the sea god, was impressed, and he gave Pelops a special chariot with very fast horses as a reward.
Classics 102 The Mycenaean Saga (Ch 18)
Poseidon then decided that he wanted Pelops to stay on Mount Olympus forever and gave him a magic chariot as a present. But Pelops left Mount Olympus and returned to mortal life, although Poseidon let him keep the magic chariot. Then he traveled to the region of Elis in western Peloponnese which was ruled by king Oenomaus who had a beautiful.